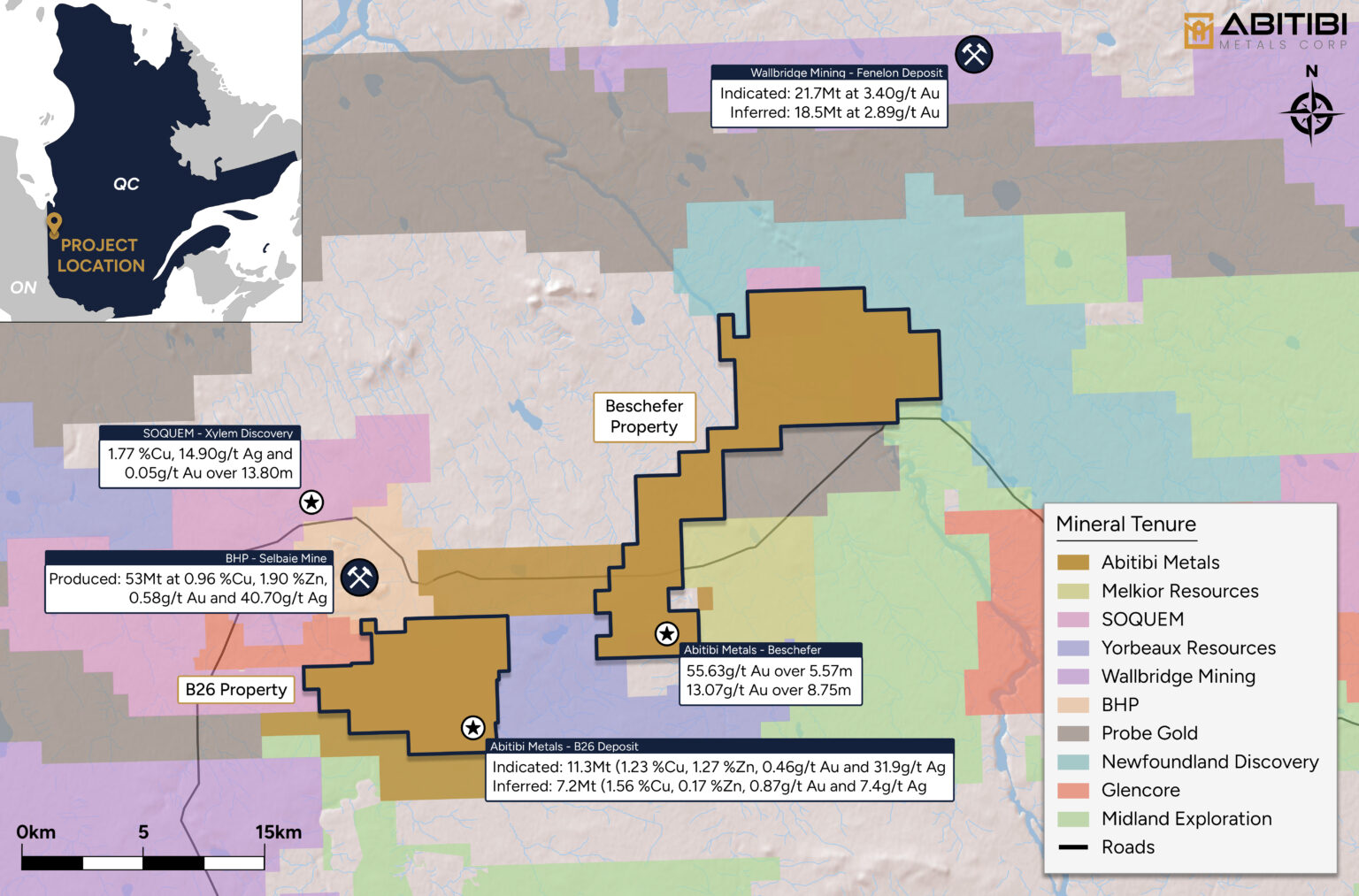
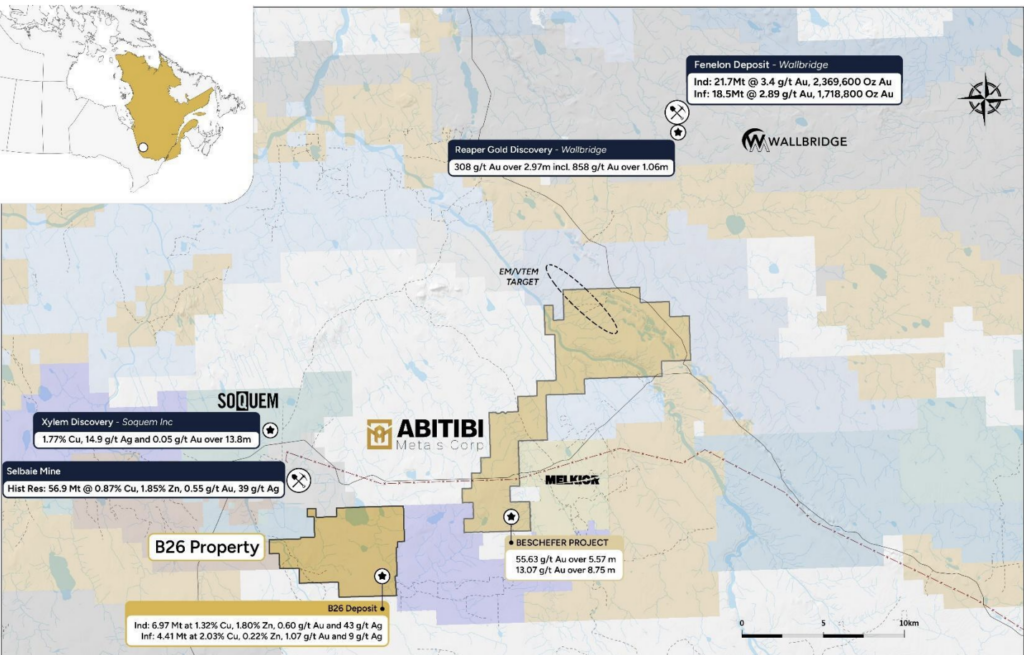
The mineralization style at B26 is composed of stacked massive and semi-massive polymetallic sulfide lenses extending over a kilometer within a strongly dipping basin filled with felsic volcanics. Sulfide-rich mineralization is mostly hosted in rhyolite and associated tuffs. Two main types of mineralization characterize the deposit. The northern part of the mineralized system is characterized by chalcopyrite veins and veinlets hosted in sericitized and chloritized rhyolite. The southern portion of the system contains mostly disseminated to massive sphalerite, pyrite and galena mineralization, hosted in a dome of massive rhyolite. The zones are stacked in a sub-parallel pattern, oriented generally east-west, and dip 87° to the south.